Key Points
- The atopic triad is a combination of allergic conditions, such as eczema, asthma, and allergies.
- Antihistamines and corticosteroids are common treatments for allergies, each with different effects on the body and ideal ways of treatment.
- Weigh the advantages of topical or oral antihistamines in treating your eczema, considering your symptoms and the side effects of the medication.
- If your symptoms worsen when using an antihistamine, you may be allergic to it, and you should stop using it immediately.
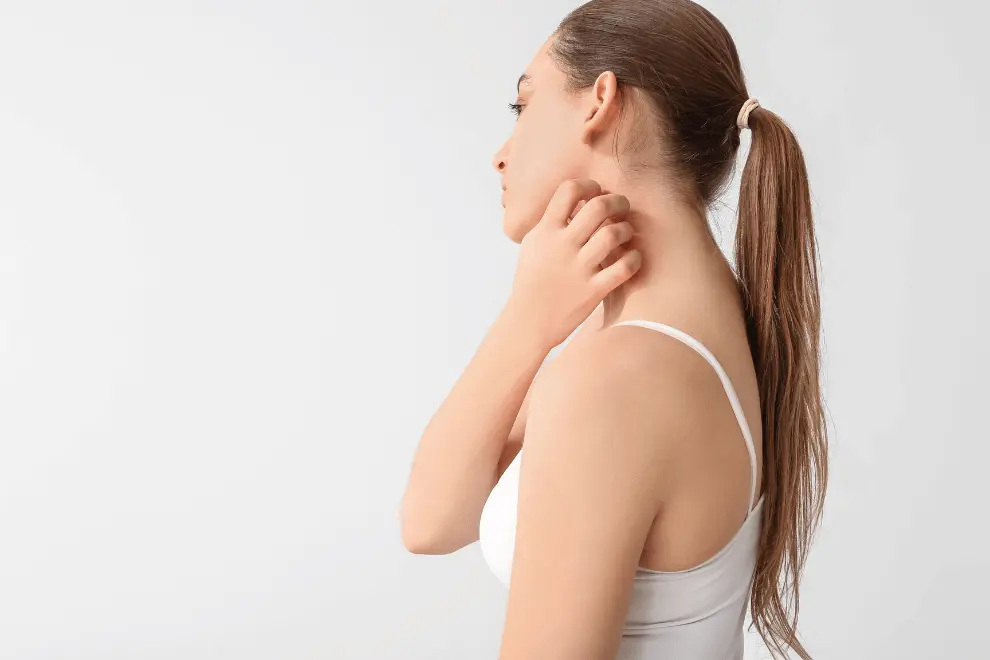
Looking for relief from eczema, asthma, and allergies? Discover how oral and topical antihistamines manage symptoms and provide itch relief. Whether you’re dealing with mild symptoms of eczema on a few patches of skin or a whole list of known allergens, antihistamines can help you find relief from your symptoms.
There are countless treatments for eczema on the market, and it’s challenging to know what is best for you until you try. Explore your options for skincare products, oral medications, topical creams, and even at-home relief methods. In July 2023, Healthline released a few DIY home remedies for eczema treatment, including an oatmeal cream to relax your stressed skin.
Atopic Triad
The atopic triad is the coexistence of three allergic conditions: atopic dermatitis (eczema), asthma, and allergies. These conditions are often seen together in people with a genetic predisposition to allergies, also known as atopy.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that causes itching, redness, and skin inflammation. Allergens, such as dust mites, pollen, or pet dander, often trigger it. Asthma is a chronic lung condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways. This makes it difficult to breathe, especially during an asthma attack.
Asthma triggers include allergens, exercise, cold air, or stress. Allergies are overreactions of the immune system to harmless substances, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. Allergies cause sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and hives.
The atopic triad comes from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of allergies are more likely to develop the triad. Ecological factors that trigger the triad include exposure to allergens, infections, and stress.
There’s no cure for the atopic triad, but there are treatments that help manage the symptoms. Treatment for eczema includes skin care products, medications, and allergy shots. Treatment for asthma includes medications, such as inhalers and steroids. Treatment for allergies includes medications, such as antihistamines and allergy shots.
Symptoms of the triad can vary from person to person, ranging from moderate to severe. Some people may only have one condition, while others may have all three. It’s most common in children but possible at any age. See a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment plan if you have any conditions that make up the atopic triad. You can manage your symptoms and live an active life with proper treatment.
Antihistamines vs. Corticosteroids
Antihistamines and corticosteroids are both medications used to treat allergies. However, they work in different ways. Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that suppress the immune system. They treat various conditions, including allergies, asthma, and arthritis. Corticosteroids are available by prescription only. Antihistamines block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body in response to an allergic reaction. Antihistamines are available over-the-counter and by prescription.
According to medical expert Stephanie Watson at WebMD, “Histamine is a chemical that your immune system releases when you’re allergic to things like pet hair, pollen, or shellfish. When histamine is released, fluid leaks from your blood vessels into your skin, which leads to swelling, a rash, itching, and other symptoms of an allergic reaction. Antihistamines block histamine to relieve the itch and bring down swelling in your skin. The sedative in some antihistamines relaxes you and makes you sleepy. By helping you sleep, these medications keep you from scratching your skin at night and irritating it even more.”
In general, antihistamines are more effective for treating mild allergies, while corticosteroids are more effective for treating severe allergies. Antihistamines are also less likely to have side effects than corticosteroids. However, corticosteroids are more effective for treating allergies affecting the nose or lungs, such as allergic rhinitis and asthma. They also prevent allergic reactions from happening.
Antihistamines can cause drowsiness, so avoiding driving or operating machinery after taking them is important. Side effects of corticosteroids include weight gain, fluid retention, and mood swings. These side effects are usually mild and disappear when you stop taking the medication. It’s essential to take antihistamines and corticosteroids as prescribed by your doctor. Don’t stop taking any medication without talking to your doctor first.
Talk to your doctor if you’re unsure which medication is right for you. They can help you decide which medicine is best for your needs.
Antihistamines for Eczema
Antihistamines help with itching in eczema by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body when exposed to an allergen or irritant. Histamine causes the symptoms of eczema, such as itching, redness, and inflammation.
When an antihistamine binds to a histamine receptor, it prevents histamine from binding to the receptor. This prevents histamine from causing its effects, such as itching. Antihistamines aren’t a cure for eczema, but they work to relieve the itching and inflammation associated with the condition. They prevent scratching, which damages the skin and makes eczema worse.
Topical Antihistamines
Topical antihistamines treat eczema by blocking the effects of histamine, such as itching, redness, and inflammation. Applying a topical antihistamine to the skin binds to histamine receptors and prevents histamine from binding to the receptors. This prevents histamine from causing its effects, such as itching.
Topical antihistamines are effective in relieving itching and inflammation. They’re usually used with other treatments, such as topical corticosteroids or emollients. However, they may not be suitable for everyone. Topical antihistamines are greasy and may not absorb well into the skin. They sometimes cause side effects, such as skin irritation.
Topical antihistamines combined with topical corticosteroids reduce inflammation and itching, with emollients to moisturize the skin and prevent dryness, or with oral antihistamines to relieve itching. The best combination of treatments for eczema varies depending on the individual.
There are a few things to consider when deciding if you should use a topical antihistamine:
- Symptom Severity: If your symptoms are mild, you may be able to manage them with over-the-counter topical antihistamines. However, if your symptoms are severe, you may need to see a doctor for prescription medication.
- Location: If your symptoms are in a small area, such as a rash on your arm, you can use a topical antihistamine. However, if your symptoms are widespread, you may need an oral antihistamine.
- Personal Preferences: Some people prefer topical medications because they’re less likely to cause side effects than oral medications. Others prefer oral medications because they’re more practical for widespread symptoms.
If you decide to use a topical antihistamine, there are a few things to keep in mind:
Some topical antihistamines can dry the skin, so choose one for your skin type. Most topical antihistamines are most effective when applied to the affected area two to three times daily. It may take a few days for the medication to take effect.
Oral Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines block the effects of histamine in the bloodstream. They relieve itching and inflammation throughout the body. However, oral antihistamines often cause drowsiness and other side effects.
Oral antihistamines are usually taken once or twice daily, with or without food. Use them alone or in combination with other treatments, such as topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching or with topical emollients to moisturize the skin and prevent dryness.
Start with a low dose of oral antihistamines and increase it gradually as needed to gauge how your body reacts and how much you need. Try taking it at night to avoid drowsiness during the day. Avoid taking the antihistamine with alcohol or other medications that can cause drowsiness. The best way to use oral antihistamines for eczema varies from person to person — talk to your doctor to find the proper treatment for you.
Allergy to Antihistamines
It isn’t common to be allergic to antihistamines. However, it’s possible to be allergic to one or more types of antihistamines. If you experience symptoms such as hives, itchy skin, difficulty breathing, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, anaphylaxis, or swelling of the face, tongue, lips, or throat, you’re likely experiencing an allergic reaction to the medication. Stop taking the medication and seek medical attention immediately.
Call 911 or visit the nearest emergency room if you have difficulty breathing, face, lips, tongue, throat swelling, or other severe symptoms. Take your EpiPen if you have one.
If you’re allergic to one antihistamine, you may be allergic to others. However, this isn’t always the case. Some people are only allergic to certain types of antihistamines. Talk to your doctor to identify your allergens and find other treatments for your eczema and allergies.
It’s important to note that not all antihistamines are equal. There are different types of antihistamines, and some are more likely to cause allergic reactions than others. If you have a history of allergies, talk to your doctor about which antihistamine is right for you. Start with a patch test when using any new product on your skin 24 hours before widespread application to ensure your skin reacts well.
Help Your Skin Recover
If you’re dealing with eczema, allergies, asthma, or the whole atopic triad, stay hopeful that there’s effective treatment for you. Seeing your immune system fight your body is scary and frustrating, but there are ways to minimize your symptoms and help you feel relief. Talk to your doctor about your options, and stay patient as you experiment with different treatments. Don’t forget to prioritize your overall well-being through a proper diet, adequate sleep, and stress relief.
Published on Age Defying September 29, 2023