Key Points
- Eczema causes red, itchy, inflamed skin, often with no known cause or trigger.
- Many auto-immune diseases, including eczema, flare up due to common food allergens.
- Track your food intake closely with your symptoms to determine which foods to eat and avoid.
- Include anti-inflammatory foods to care for your body and control eczema flare-ups.
To control your eczema, it’s important to understand its contributing factors, identify possible triggers, and adjust your diet to alleviate symptoms and avoid flare-ups. Eczema is an umbrella term for a chronic skin condition that causes the skin to become red, itchy, and inflamed.
Eczema’s cause is unknown, but it’s thought to be due to genetic and environmental factors. Triggers for an eczema outbreak are unique to each person. The most common are soaps, detergents, cosmetics, dust, medications, pollen, environmental changes, stress, foods, and other allergens that kick your body’s immune response into high gear.
If you struggle with eczema, it’s vital to identify what causes a flare-up and to avoid these conditions. Take preventive measures and implement treatments into your routine to alleviate and control your symptoms. Many find using a body wash for eczema calms, soothes, and heals the skin.
Eczema is a chronic condition, but you don’t have to suffer. Know it, treat it, control it.
Common Food Triggers
Some foods may trigger eczema flare-ups in people who are allergic or sensitive to them. These foods cause an immune reaction that leads to inflammation in the skin. Not everyone with eczema is allergic to foods. Some have food sensitivities, which means they react to certain foods even though they aren’t allergic. Food sensitivities can also cause inflammation, leading to eczema flare-ups.
The most common food allergens that trigger eczema include:
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Peanuts
- Tree nuts
- Soy
- Wheat
- Shellfish
While less prevalent, these foods also act as triggers:
- Citrus fruits
- Tomatoes
- Chocolate
- Coffee
- Alcohol
- Spicy foods
- Foods with artificial colors or flavors
Everyone has their own sensitivities and allergies. Identifying yours lets you take better care of your body, reduce your immune responses, and have less eczema.
Finding Your Food Triggers
You don’t have to cut all those amazing foods out and eat a restricted, bland diet for your whole life. Simply identify which foods negatively affect your body. There are a few methods to figuring out which food is your kryptonite.
Food Diary
Keeping close track of the foods you eat and the way your body feels is a fantastic tool for determining which foods are good and bad for your body. If you want to take it an extra step, record your stress levels, amount of sleep, start a daily skincare routine, and other factors that might affect your eczema or health.
There are many ways to keep a food diary. You can use a notebook, a food journal app, a piece of paper, or the notes app on your phone. Choose a comfortable method and stick with it. The hardest part about keeping a food diary is consistency with your recording.
Record the information on your phone if you forget your notebook. If you don’t have the patience to write your food intake each time you eat, take a photo of your meals and snacks and write them down in an organized manner later. Observe trends and connections between the ingredients you consume and your eczema symptoms.
After a few weeks of diligent recording, the culprit or culprits become apparent. Present your food diary to your dermatologist or the doctor treating your eczema. They can pinpoint trends and symptoms and guide you on how to avoid allergens.
Elimination Diet
Talk to your doctor about developing and following an elimination diet to manage your eczema. An elimination diet removes foods to see if they’re causing problems. This benefits eczema sufferers because it identifies foods that trigger symptoms.
To follow an elimination diet, start by making a list of all the foods you typically eat. Remove one food group for two to four weeks. Start with common allergens or those you suspect of contributing to your eczema symptoms.
Keep track of symptom changes during each elimination period. If symptoms improve when you remove a particular food group, then that food group may be the trigger. After identifying the suspected cause, slowly reintroduce it to your diet to see if your symptoms return. If they do, avoid that food group to protect from potential flare-ups.
Elimination diets are beneficial but challenging to follow. You must be patient and consistent when following an elimination diet. It takes time to identify the food group causing your symptoms. Sometimes there’s more than one. When this question is answered, avoiding those foods lets you manage your condition.
Consuming the suspect food during an elimination period skews your results and makes it difficult to accurately determine your body’s response. Remove only one food at a time. Removing too many potential culprits simultaneously makes deciding which one is causing your symptoms more challenging.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Health and medical experts at Harvard Health say, “Doctors are learning that one of the best ways to reduce inflammation lies not in the medicine cabinet, but in the refrigerator. You can fight off inflammation by following an anti-inflammatory diet.”
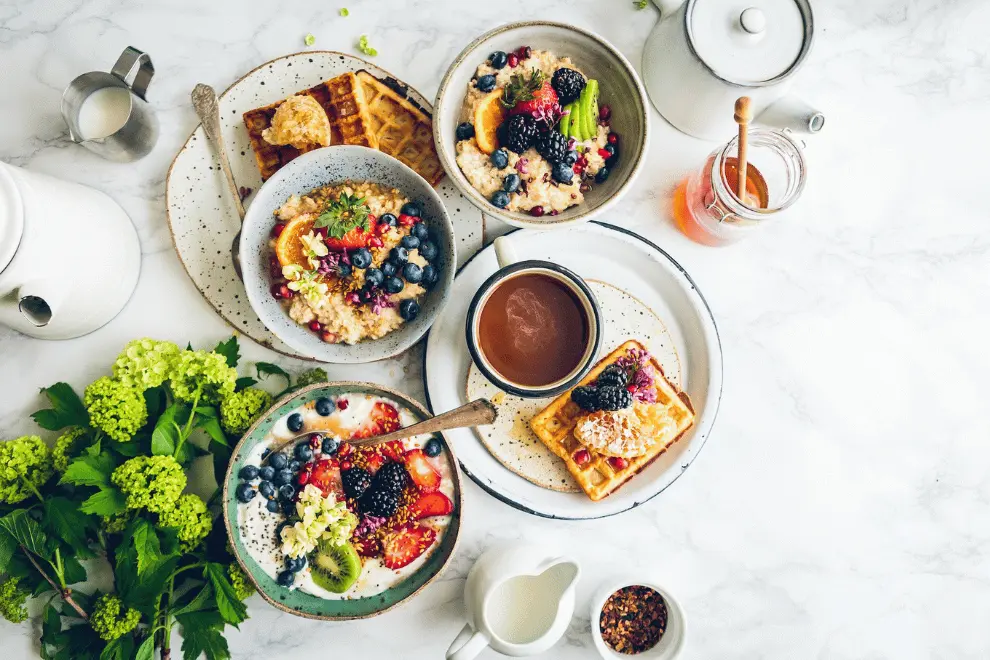
Create an eczema-friendly diet as you remove foods that trigger your symptoms and add foods that potentially limit the inflammation in your body. An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on eating foods that reduce inflammation in the body. This approach is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. It limits processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
Your doctor or dietician can recommend a well-balanced diet, including these foods. You don’t want to ride a unicycle in the race against eczema. That vehicle has three more “wheels”: drink sufficient water, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
These lifestyle factors reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are a good source of antioxidants, which reduce inflammation. Berries are incredibly high in antioxidants to reduce inflammation. Other good choices include leafy greens, citrus fruits, and tomatoes.
Leafy greens, such as kale and spinach, are full of antioxidants and are also high in fiber that regulates digestion and reduces inflammation. Citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits are rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant that protects the body from damage. Tomatoes are a good source of lycopene, an antioxidant with anti-inflammatory effects.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are also fiber-rich. Brown rice also has magnesium, which reduces inflammation. Quinoa is a good source of protein and iron, while oats provide fiber and beta-glucan, a soluble fiber with anti-inflammatory effects.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats like those in olive oil, avocados, and nuts reduce inflammation and keep the skin healthy. Olive oil is a healthy source of mono-unsaturated fat. Avocados are rich in mono-unsaturated fat and fiber. Nuts provide polyunsaturated fat. These healthy fats’ anti-inflammatory effects reduce symptoms of eczema and other inflammations in the body.
Lean Protein
Lean protein, such as chicken, fish, and beans, keeps the body healthy and reduces inflammation. Chicken is a good source of protein and is low in saturated fat. Fish provides protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Beans are a complete protein and fiber source, offering anti-inflammatory benefits.
Spices
Spices like turmeric and ginger have anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric is a good source of curcumin, and ginger is a good source of antioxidants. Ginger and turmeric have been trusted for centuries to treat various illnesses and ease inflammation.
To incorporate anti-inflammatory spices into your diet, make golden milk — a warm, delicious drink with outstanding benefits. Try the June 2023 golden milk ice cream recipe for a cold treat!
Regain Control of Your Body
Creating a balanced diet, eliminating allergen triggers, and nourishing your body with anti-inflammatory foods works wonders on your body and your eczema. A balanced diet reduces inflammation, improves skin barrier functions, provides essential nutrients, boosts your immune system, and improves overall health.
Each benefit improves your eczema symptoms and leads you to a more comfortable life!
Published on Age Defying September 29, 2023